Google receives around 63,000 searches every second, but have you ever wondered how it processes these requests?
The Google “brain” so to speak is ever-changing and can be seen gathering large amounts of data at any moment. Google has evolved and become more sophisticated over the years and is now able to process natural language making informed decisions on what the consumer base is looking for. Below, I will discuss how linguistics plays into this process, touch on singular versus plural duality and the importance of user intent when applying SEO strategy to site content or paid search.
How Google Interprets Linguistics & Natural Language
Since Google’s inception, it has come a long way with interpreting what humans want. Beginning as a system merely dedicated to checking backlinks to estimate the importance of sites, it has evolved into a warehouse of data and information devoted to learning what users truly want.
Increasing in sophistication, Google now weighs human dialect heavily in order to process language to show SERPs that are highly relevant. These linguistics adaptations married to user intent, create a much more enjoyable and useful platform allowing Google to be the household owner of the search landscape making frequent updates to match query needs.
How do they accomplish this?
Consistent. Updates.
BERT Update
In a statement from Google, “by applying BERT models to both ranking and featured snippets in search, we’re able to do a much better job helping [users] find useful information. In fact, when it comes to ranking results, BERT will help Search better understand one in 10 searches in the U.S. in English, and we’ll bring this to more languages and locales over time,” allowing Google to capitalize on colloquial and conversational tones to find out what we really want (Google Blog).
Check out Zaine’s fantastic breakdown on the BERT update to go in-depth and learn how this looks like in the SERP landscape.
Key Takeaway: Google is evolving through analyzing natural language data and user actions
How Can We Apply Linguistics to SEO Strategy?
By marrying user intent with linguistic preferences, SEOs can optimize sites to answer consumer need. Below are a few ways to begin accomplishing this task:
1. Conduct Linguistics Research for Your Site
Begin research by using your favorite SEO tool to look at syntax, grammar and vocabulary matched with search volume to get a sense of how people are searching.
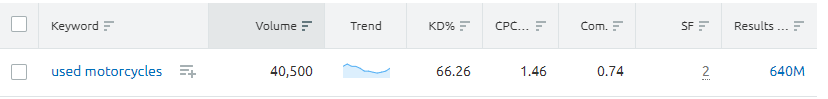
For example, look at the difference between “used motorcycles” versus “pre owned motorcycles”
Look at what your site is already ranking for and bridge the opportunity gaps. Check the search landscape by typing these keywords into Google to get a feel for the landscape and language tone.
Ask yourself:
- Are these surrounding results applicable to my site/landing page?
- Does this align with my messaging?
- Are these users approaching this with the intent to buy or educate themselves?
2. Optimize for Plurality & Singularity to Capture SERPs
Why does this matter?
When it comes to singulars and plurals, there are many words that might hold different meanings leading to extremely different search results. As a simple example, take the word “driver” versus “drivers.”
These two words have drastically different search results. To make it even more complicated, adding adjoining words can alter those results even further. As seen below, the keyword “glass” tells Google to show movie and hardware results, whereas the plural “glasses” shows an emphasis on the eyewear.
Why Would Google Show Different Results?
It all comes down to linguistics & user intent.
When looking at the linguistics of search queries, one must always go back to the “why” behind user searches. Where do target consumers spend their time and what are they truly seeking?
With the changes between singular and plural altering entire meanings of words, comes a large shift in user intent across many industries. This pushes us to dig deeper into how to identify consumer intent by understanding language on a more intricate level.
How To Apply This To SEO & Paid Campaigns:
- Always speak in natural language
As mentioned before, Google is evolving and getting smarter. Speaking to customers the way they would be searching for your service or product is always crucial for identifying user intent.
- Look at the meaning of certain keywords and run through SEMrush to see what the SERPs are showing
Many words have a similar meaning and therefore lead to cross-over, but for keywords on the fence, it is always best to take a look at the singular and plural variations ~in the wild~ and then optimize accordingly.
If there are more searches on singular keywords and you are targeting plurals, you may be missing out on the chance to rank for singulars as well. Best practices always recommended to optimize for both, but doing this extra step to look at the variations may save you money in ad campaigns by finding less-competitive & more optimal spaces for bidding.
Key Takeaway: Always go back to user intent and check the SERPs!
3. Use Natural Language Processing to Understand Content (Like Google Does)
Dan Shankle, did an excellent presentation on this concept so I thought I would share some highlights to help to further explain the intricacies of Google’s interpretations.
What is NLP?
Natural Language Processing is the way in which Google understands intent. It ultimately comes down to how it segments users asking “why does it” versus “why is my” and highlights the neural matching needed to dive deeper into intent.
How Does It Do This?
Ultimately, Google crawls content for entities and salience. Entities being the people, numbers, metrics, etc. within the content and salience pertaining to the summation of the content in order to provide a link to understand their relationship.
To explain entities, Dan used the example of a cookie recipe seen below:
“Entities for Cookie Recipe: All ingredients and instructions (flour, eggs, milk, mixing, bake time, bake temp).
How Can We Leverage This as SEOs?
- Connect questions to answers
- If someone is asking for instructions on how to make a paper plane, don’t begin with a long story about how you came to learn about the art form, but rather begin with the answer and expand later. People value immediacy over length.
- Be specific and explain nuances
- Using Dan’s cookie example, provide specific, useful answers to consumer questions as seen below:
- Question:“What is the best temperature to bake chocolate chip cookies?”
- Answer:“The best temperature to bake chocolate chip cookies is usually between 325 and 425 degrees, depending on your altitude and how crisp you like your cookie.”
- The more specific the better.
- Link your entities!
- In order to link entities together, move them closer together. Reduce the semantic hops the robot has to jump. This can be established by eliminating fluff and clutter that further your entities’ connection and ultimately makes it easier for Google to understand what the content is about.
- Use APIs to Understand Natural Language Processing
- Two APIs that you can use include:
- The Google API aims to use “machine learning to reveal the structure and meaning of text. You can extract information about people, places, and events, and better understand social media sentiment and customer conversations. Natural Language enables you to analyze text and also integrate it with your document storage on Cloud Storage,” through insightful text analysis (Google Cloud).
- The goal of APIs is to understand the strength of entity and salience bonds by seeing how they are being interpreted through semantic machine learning.
- Using Dan’s cookie example, provide specific, useful answers to consumer questions as seen below:
Key Takeaway: Connect Entities to Salience & Answer Consumer Questions!
User Intent Is How You Win
At the end of the day, knowing what the user intends to find is how you will win the game. Going the extra mile to investigate linguistics may lead you to find more competitive spaces to penetrate with both your SEO and Paid strategy.