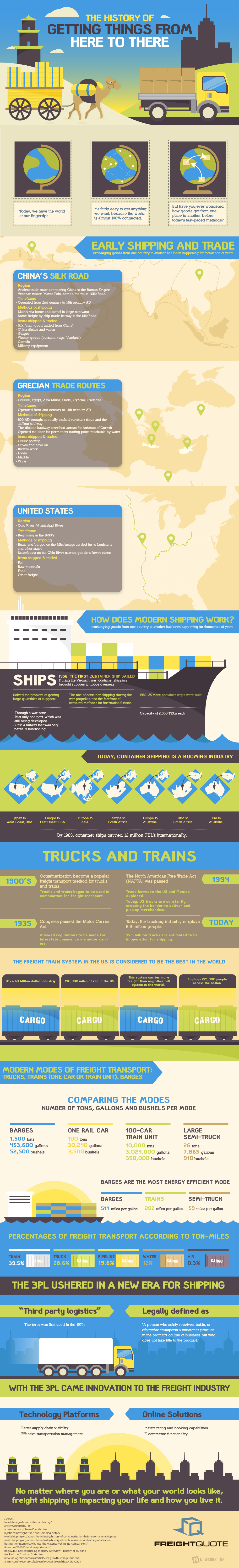
Since ancient times, people have needed to haul cargo from one place to another. In ancient China, the Silk Road was the main mode of transportation for things like silk, dishes and pottery, grapes, woolen goods and rugs, military equipment, and camels. Yes, they both traded camels and used camels to transport goods. Trade operated this way until about the 14th century.
During the same timeframe, Ancient Greek traders took to the Mediterranean Sea in specially designed merchant ships, creating the diolkos haulway. This gave way to permanent trading ports that were reachable by water. People near these ports had access to olives and olive oil, Greek pottery, bronze, hides, marble, and wine.
In the early days of the United States, waterways were the superhighways of their time. Fur traders began to use the Ohio and the Mississippi Rivers in the 1600s to transport furs to Louisiana for sale in Europe on flat boats. Later steamboats moved cargo such as food, raw materials, bourbon whiskey, and other items up and down the river.
Now in the modern age, things are shipped in cargo containers most of the time. This is a versatile way to move things from one place to another because the containers can be used on cargo ships, on rail cars, and pulled with semi-trucks. The first container ship sailed in 1956, and now the ships are even bigger than ever. The American Freight Train system is considered to be the best in the world—one rail car can haul as much as 100 tons of cargo. Barges are still used in the nation’s waterways, and are the most energy-efficient way to transport cargo at 514 miles per gallon of fuel. Cargo trains are close behind them at 202 miles per gallon, and semi-trucks are a distant third at 59 miles per gallon. Almost 40% of cargo in the United States is transported by train, and nearly 30% is transported by truck.
You may not realize it, but there are a lot of rules and laws that govern the transportation of goods. What if you are a truck driver and your load is damaged before you pick it up? There have to be rules about who is to be held responsible. Third party logistics was developed in the 1970s to outline some of these rules, and other rules are outlined in trade agreements. Technology has also revolutionized the shipping and logistics industries by giving everyone real-time data about the supply chain. Learn more about the history of shipping throughout the world from this infographic.
Source: http://info.freightquote.com/freightshippinghistory
Author: NowSourcing is an award-winning nationally recognized infographic design agency. Founded in 2005, NowSourcing has strong roots in the human and technical nuances of the web.