3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, offering an innovative way for small businesses to create products efficiently and cost-effectively. This technology, once the domain of large corporations, is now accessible to smaller enterprises that wish to harness its potential. However, it’s necessary to consider these common challenges of 3D printing in bulk to ensure they don’t slow you down.
Inconsistent Extrusion
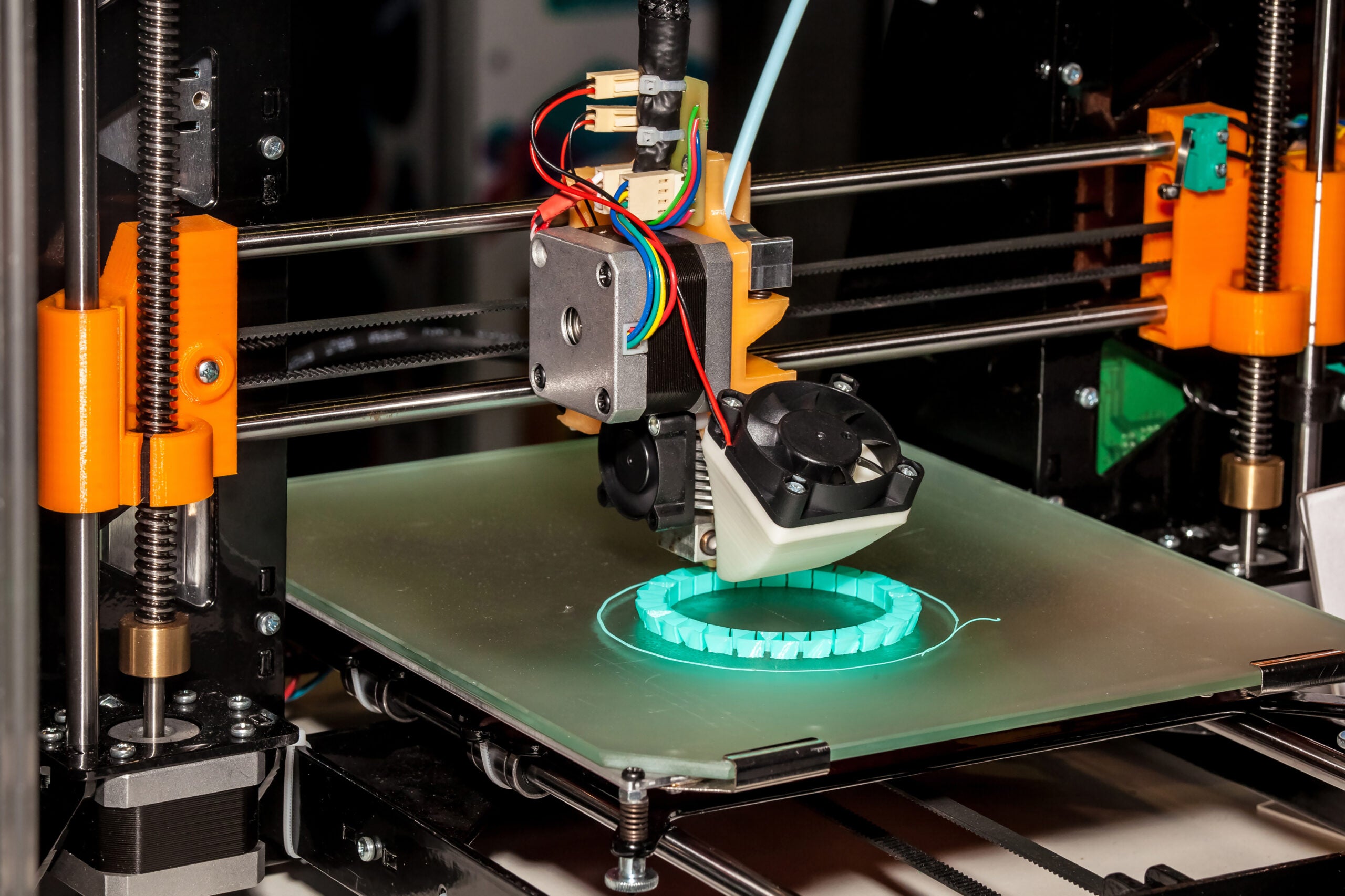
Inconsistent extrusion is one of the most prevalent hurdles encountered in bulk 3D printing. This issue can lead to uneven layers, filament leakage, or complete print failures, ultimately affecting the final product’s quality and appearance. Several factors contribute to this challenge, including fluctuations in temperature, filament quality, and the printer’s calibration settings.
Therefore, operators must regularly monitor and adjust their machines, ensure the use of high-quality filament, and maintain a stable printing environment. Implementing these measures can significantly reduce extrusion problems, ensuring consistent and reliable production.
Layer Separation
 Layer separation, also known as delamination, is another common issue encountered in bulk 3D printing that can compromise the printed object’s structural integrity. This problem arises when there is inadequate adhesion between the printed layers, leading to cracks or complete separation. Several factors can cause layer separation, including incorrect temperature settings, insufficient cooling, and material mismatches.
Layer separation, also known as delamination, is another common issue encountered in bulk 3D printing that can compromise the printed object’s structural integrity. This problem arises when there is inadequate adhesion between the printed layers, leading to cracks or complete separation. Several factors can cause layer separation, including incorrect temperature settings, insufficient cooling, and material mismatches.
Fine-tuning the printer’s temperature settings is essential for ensuring optimal adhesion. Additionally, ensuring the proper cooling of each layer can prevent them from warping or pulling apart. Selecting the right materials that are compatible with the printer and adjusting the print speed can also address layer separation.
Material Limitations
The choice of material heavily influences the final product’s strength, flexibility, and durability. Some 3D printing facilities use materials such as PLA due to their ease of use and biodegradability; however, they may lack the strength required for certain applications. On the other hand, materials such as ABS or nylon offer greater stability and heat resistance but can be more challenging to print. Additionally, they require specific environmental conditions, and some high-performance or specialized materials may not be economical for bulk production due to their cost. Businesses must carefully consider the material properties required for their application, balancing cost and performance for efficient and effective bulk production.
Knowing what to do if your 3D printer is overheating or experiencing other common problems isn’t just a helpful skill; it’s knowledge that can keep your manufacturing operations running smoothly. These common challenges of 3D printing in bulk are not insurmountable, and with the right approach, businesses can overcome them to achieve successful and cost-efficient production. By regularly maintaining and calibrating their machines, selecting suitable materials for their applications, and fine-tuning printing settings, small business owners can harness the full potential of 3D printing in bulk.
721 Views












